Cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into lifesustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water It includes glycolysis, the TCA cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation · Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and then release waste products The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing · Cellular respiration is the process by which cells in plants and animals break down sugar and turn it into energy, which is then used to perform work at the cellular level The purpose of cellular
Cellular Respiration Vs Photosynthesis Mrs Thomas Classes
Model of cellular respiration simple
Model of cellular respiration simple-Comparative physiology of vertebrate respiration Vertebrates Respiration;2 $175 Google Forms™ This ten question, self grading quiz for middle school science assesses students' knowledge on the purpose of photosynthesis and cellular respiration, the reactants and products of each process, what organelle the process occurs in, and the type of organism that performs each process All the questi




Model Cellular Respiration
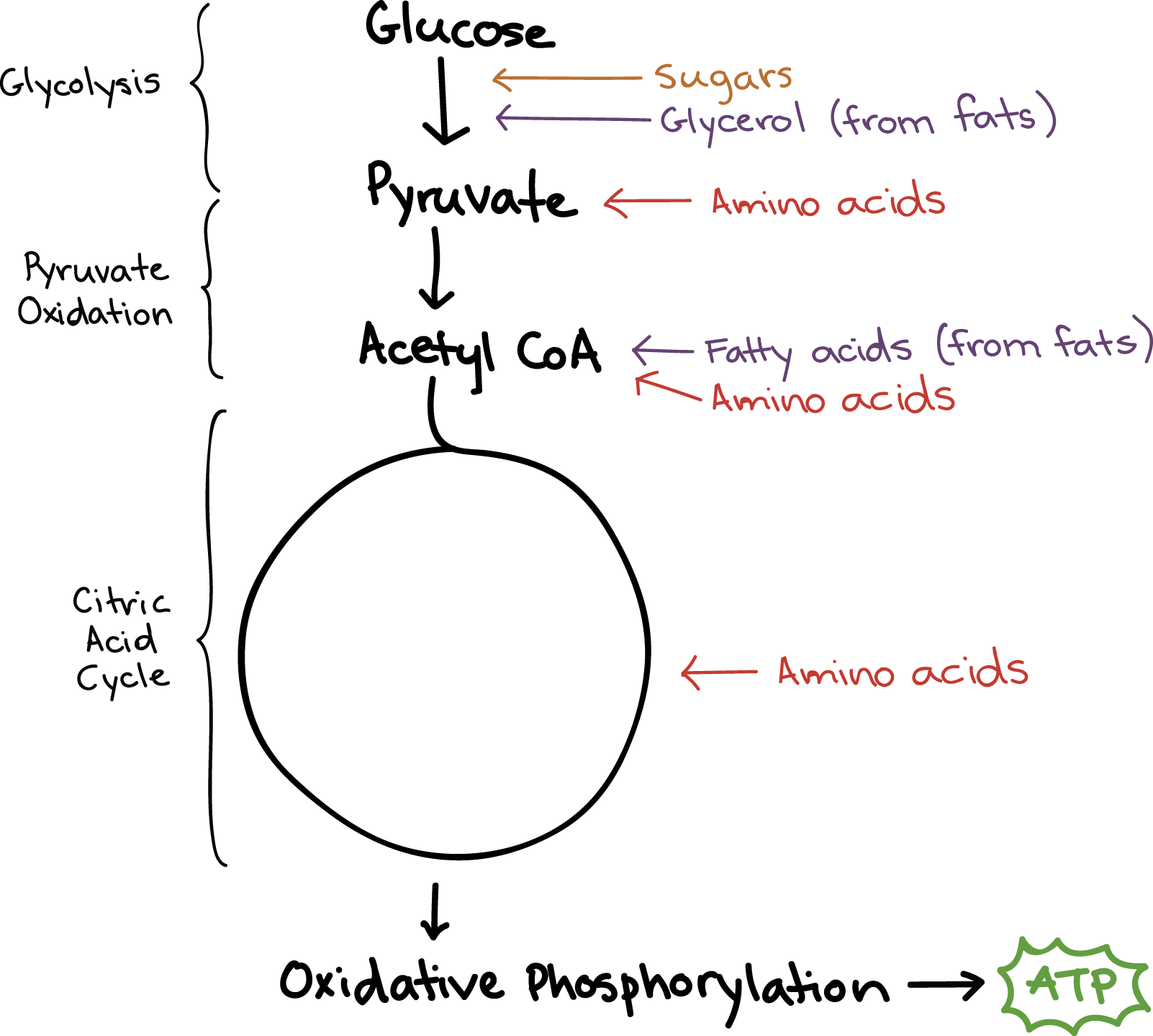
/10/16 · The protein is further broken down into amino acids that are used in restocking the cells and manufacturing new cells Cellular Respiration can be summarized as Glucose Oxygen= Carbon Dioxide Water ATP (Energy) Cellular Respiration in PlantsMolecular Models of Photosynthesis and Respiration Build molecular models that illustrate key principles of energy transfer through the chemical reactions of photosynthesis and respiration Also, use a model to show how carbohydrates can be used to build other important biomoleculesVideo This is a fun, easy way to teach photosynthesis and cellular respiration with a simple handson model The details can be taught later, but this model establishes the basic principle that photosynthesis traps energy into a form that organisms can
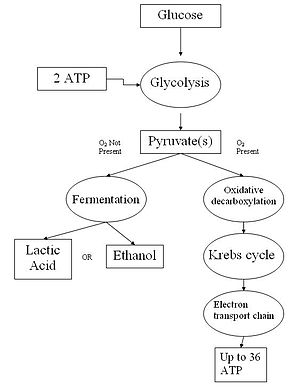
Cellular respiration is a process that takes place within the cells of organisms where energy is released by breaking down the chemical bonds of glucose (C6H12O6) The energy released is in the form of ATP molecules that are used to carry out various functions of the cell The cellular respiration equation is as followsCellular Respiration 1 Overview Cellular Respiration 1 Overview Watch later Share Copy link Info Shopping Tap to unmute If playback doesn't · The Reactions of Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Breaks Glucose Down Gradually All at once = energy wasted as heat Occurs in several steps 10 Complete Breakdown of Glucose is
CELLULAR RESPIRATION SIMPLIFIED /// Cellular respiration simplified In this video I provide an introduction to respiration and cellular respiration Fancy a · Steps Of Cellular Respiration (1) Glycolysis Glycolysis is the first step in the chain of catabolic reactions the comprise the process of cellular respiration During glycolysis, monosaccharides (simple sugars) such as glucose, sucrose, orIn this kinesthetic model, students will learn that plants need carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight to carry out photosynthesis Using ping pong balls and egg cartons, they will simulate the production of sugar molecules to store energy (photosynthesis), and then break apart these molecules to acquire energy (cellular respiration)



Cellular Respiration Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia




Cellular Respiration Diagram Biology Wise
Students will use their Cellular Respiration Lecture Notes from the previous lesson and their Photosynthesis Lecture Notes from a prior lesson in the beginning of the Cell Energy Unit to connect their understanding of photosynthesis and cellular respiration Students will design a model that depicts the photosynthesis and cellular respiration as the processes cycle carbonCellular respiration is a common process that is carried out by many organisms to make and release energy It is basically a process through which the cells covert glucose and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water, and hence release energy for ATP ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate and is the free energy that is used by cellsColor Model, B&W Handout, Labeling Quiz Cellular Respiration in Plants 1) Photosynthesis creates glucose molecules (instead of eating) → 2) This fuels cellular respiration in the plant cells → 3) Creates ATP → 4) Fuels plant growth and reproduction → 5) Provides carbohydrates to animals for their cellular respiration




Core Principles Which Explain Variation In Respiration Across Biological Scales O Leary 19 New Phytologist Wiley Online Library




Cellular Respiration 1 Overview Youtube
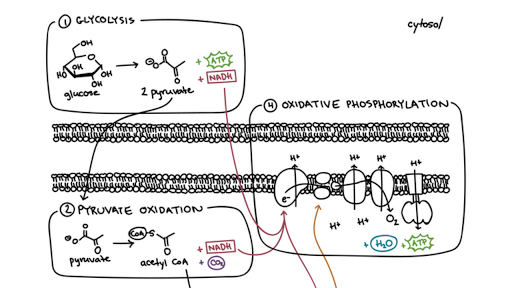
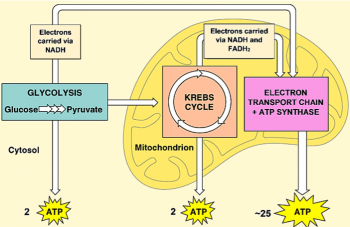
· Glucose is a simple carbohydrate with the chemical formula It stores chemical energy in a concentrated, stable form In your body, glucose is the form of energy that is carried in your blood and taken up by each of your trillions of cells Cells do cellular respiration to extract energy from the bonds of glucose and other food moleculesStudents analyze two models of cellular respiration – chemical equations that summarize the inputs and outputs of cellular respiration and a figure that summarizes the three major stages of cellular respiration (glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain plus ATP synthase) Students use what they have learned to develop their own · Cellular respiration can be described by a simple 'formula' that encompasses all of the factors that play a role in the process The formula above starts out with oxygen and a sugar, glucose, on the left hand side, and through a series of reactions and processes that make up cellular respiration, we are left with the end results (right side)




Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Project By



Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration At The Atomic Level Lesson Teachengineering
Cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy Autotrophs (like plants) produce glucose during photosynthesis Heterotrophs (like humans) ingest other living things to obtain glucose While the process can seem complex, this page takes you through the key elements of each part of cellular respirationPhysiology, Comparative CELLULAR RESPIRATION 127 action of the cytochrome system may be indicated in the diagrams below which show how a substrate to be oxidised (AH2) reduces the cytochrome and is itself oxidised in the presence of a specific dehydrogenase enzyme3) HSLS17 From Molecules to Organisms Structures and Processes Target Use a model to illustrate that cellular respiration is a chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and the bonds in new compounds are formed resulting in a net transfer of energy Help/FAQs



Steps Of Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy



Do Plants Breathe Nsta
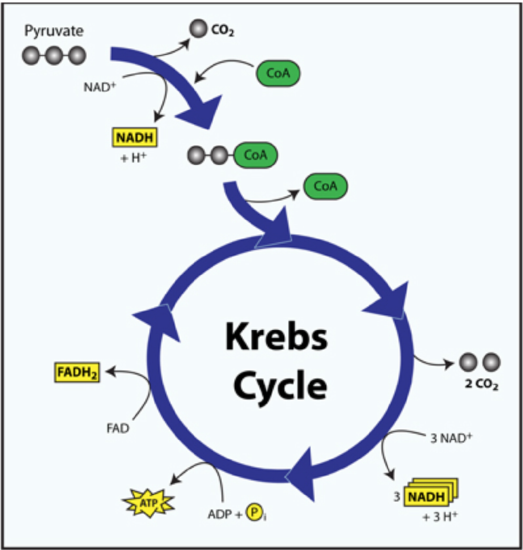
Overview of the steps of cellular respiration Glycolysis Sixcarbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each) ATP and NADH are made These reactions take place in the cytosol Pyruvate oxidation Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a twocarbon molecule bound to coenzyme A, called acetyl CoACellular Respiration Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organismCellular respiration, a common topic among introductory and cellular biology curricula, is a complex biological process that exemplifies core biological concepts, including systems, pathways and transformation of energy, and structure and function relationships




Ap Bio Unit 3 Study Guide Cellular Respiration Fiveable



E Coli Student Portal Aerobic Respiration
Cellular respiration is what cells do to break up sugars to get energy they can use Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create ATP, a chemical which the cell uses for energy Usually, this process uses oxygen, and is called aerobic respiration It has four stages known as glycolysis, Link reaction, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain This produces ATPCellular Respiration Select an animation Cellular Respiration The Big Picture Cellular Respiration Glycolysis Cellular Respiration The Citric Acid Cycle Cellular Respiration The Electron Transport ChainExplain to the students that the rope represents the cell membrane Also, explain that like every model, it is imperfect as the cell membrane would be 3D rather than 2D Ask the students what the function of cellular respiration is They should remember that energy production from food is the function of cellular respiration




Anaerobic Respiration The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
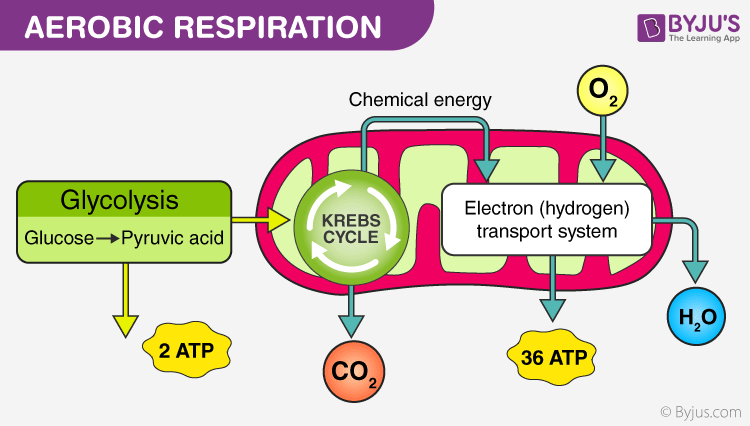



What Is Aerobic Respiration Definition Diagram And Steps
· cellular respiration enzymatic release of energy from inorganic and organic compounds Upload media Wikipedia Instance of biological process Subclass of energy derivation by oxidation of organic compounds · Cellular Respiration gives both plant and animal cells the useable energy, aka ATP, that they need to do stuff This is the overall equation C6H12O6(glucose) 6O2 → 6CO2 6H2O ≈38 ATP · Aerobic respiration is the type of cellular respiration that requires the presence of oxygen Among all the types of cellular respiration it is the most efficient Plants and animals carry out this kind of respiration;




Model Cellular Respiration




Cellular Respiration Process Download Scientific Diagram
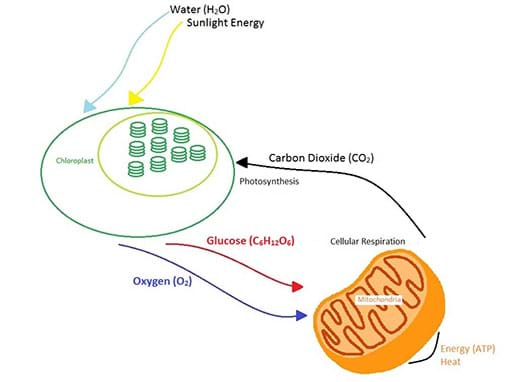
Plants obtain the precursor molecules from photosynthesis while animals obtain them from the food they eat (ie plants/animals) · This is a handson activity that is used to visualize the chemical processes Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration The attached sheet guides students through the process, and has many simple (assessable) steps needed to process through the activityCellular respiration is a process that is undergone in cells to break down molecules and produce ATP The energy released from the broken down molecules are a result of spontaneous catabolic reactions The most basic 3 metabolic stages within an animal cell are separated as followed glycolysis, the Krebs Cycle, and the Electron Transport chain




Cellular Respiration In Yeast Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
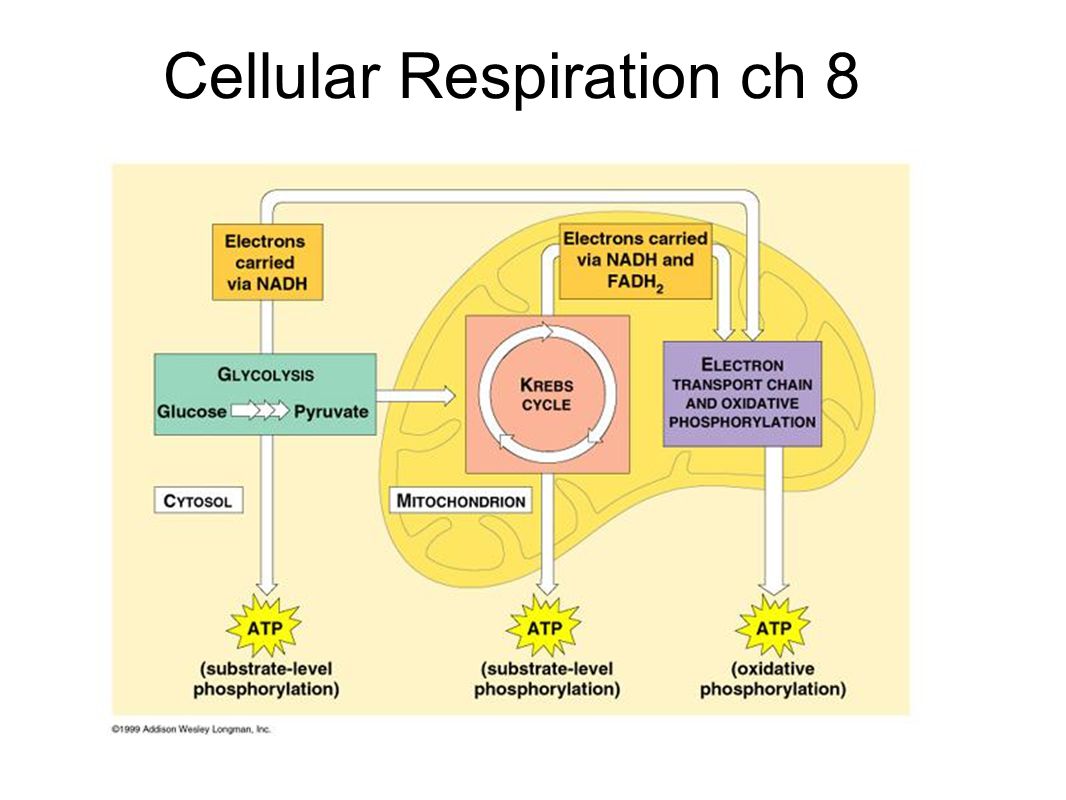



Cellular Respiration Ch 8 Ppt Download
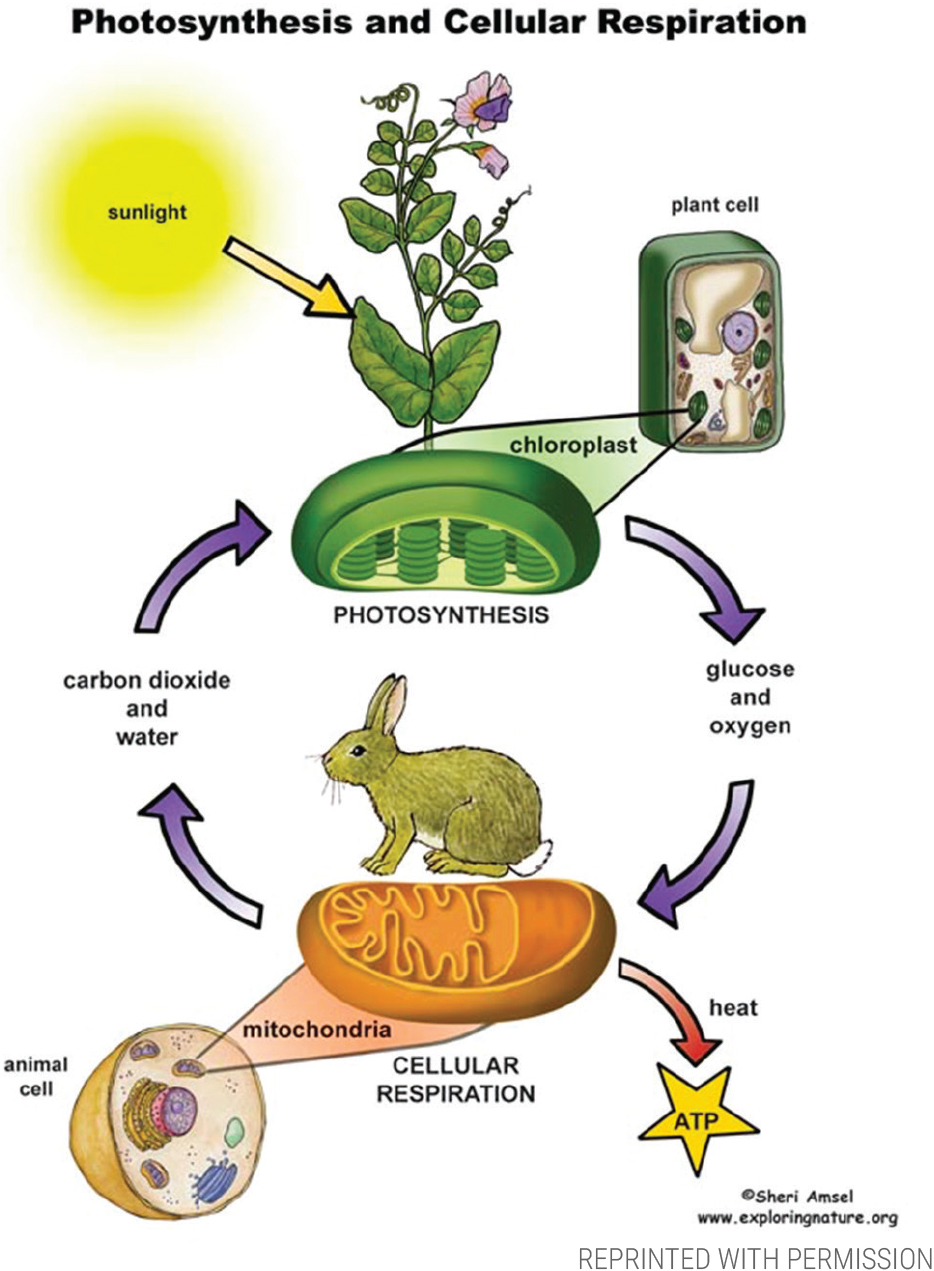
Teaching Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Using The 5E Model Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two of the most important processes on earth Without them, life couldn't exist However, they're topics that can be difficult to teach without going into too much or too little depth Finding that sweet spot can be tricky · Use a model to illustrate that cellular respiration is a chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and the bonds in new compounds are formed resulting in a net transfer of energy SP2 Developing and using models XCEMHS2 Changes of energy and matter in a system can be described in terms of energy · The products of photosynthesis are the reactants of cellular respiration and vice versa Give students 15 to minutes to work within their lab group to create a third diagram The students may create a diagram similar to the one shown in Figure 3 Figure 3 Handdrawn diagram of how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are connected



Module 2 Part B Cell Function And Energetics




Cellular Respiration Ck 12 Foundation
Cellular respiration is the process of using oxygen in the mitochondria to chemically break down organic molecules such as glucose This releases the energy stored in the bonds of glucose In this process, molecules of water and carbon dioxide are released as waste products This series of reactions produces 36 molecules of ATP!Metabolic pathways that contribute to the production of ATP molecules in cells are collectively referred to as cellular respiration When a molecule of glucose undergoes aerobic cellular respiration, 36 molecules of ATP are produced Glucose is an energyrich molecule The breakdown of glucose results in the formation of lowenergy molecules and energyCELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY NOTE It is expected that you have studied this topic in High School Biology This subject may not be covered in the lectures, but you are responsible for all of the information in these notes because it is important background for topics in this course, suchas muscle cell physiology (Chapter 7) Please be familiar with this material before we reach those
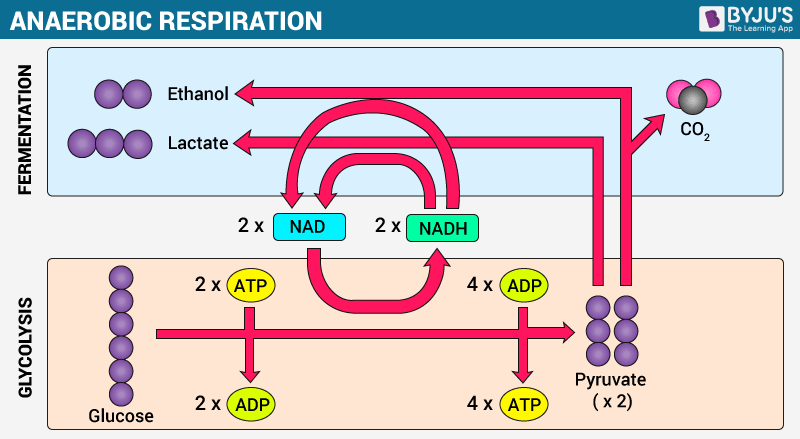



Overview Of Cellular Respiration Aerobic Anaerobic Respiration




A Beginner S Guide To Aerobic Cellular Respiration And Its Stages Biology Wise
Sep 28, 19 Explore Kathy Holfelder's board "Cellular Respiration" on See more ideas about cellular respiration, biology classroom, teaching biologyTHE BIG PICTURE 5 CELLULAR RESPIRATION The physical act of breathing and the process of cellular respiration share reactants and products But cellular respiration refers to 6 REQUIREMENTS OF RESPIRATION Cellular Respiration RequiresHere, we describe how we have adapted the children's board game Mousetrap TM (Hasbro, Milton Bradley) as a manipulative model to teach cellular respiration in our General Biology I lecture classroom In brief, the pieces of the board game are reassigned into the three stages of cellular respiration (Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain/Oxidative Phosphorylation)



Cellular Respiration Stem Resource Finder



The Tca Cycle
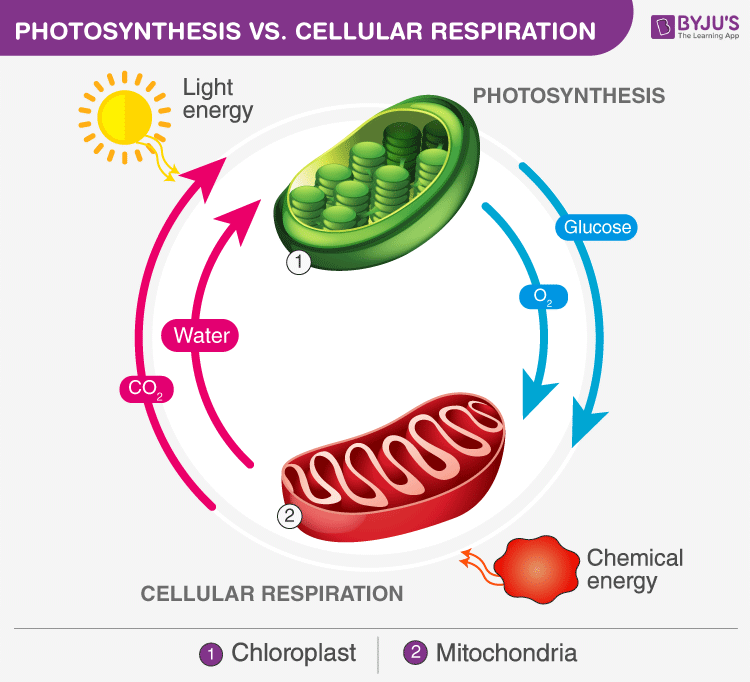



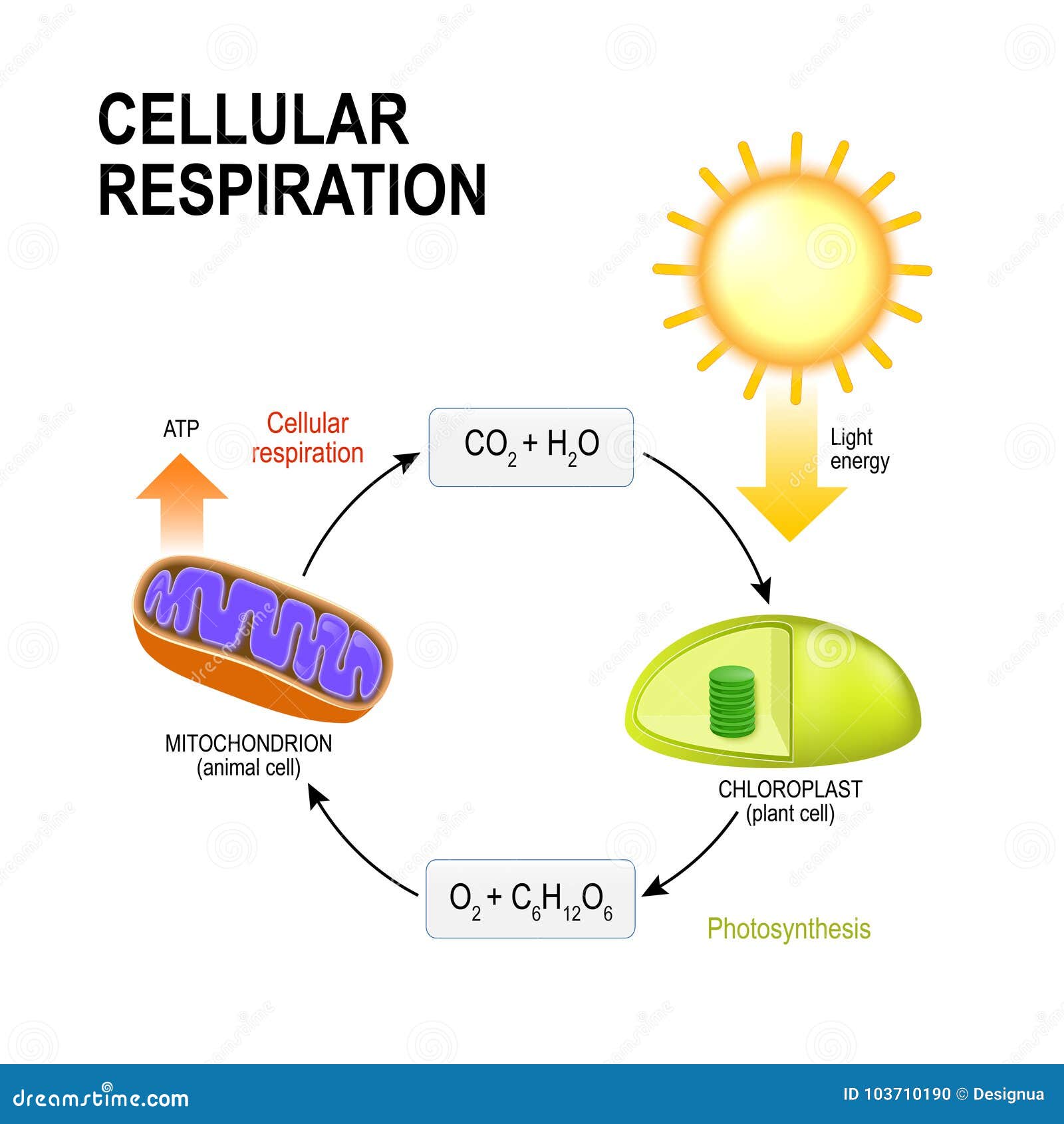
Differences Between Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis




Aerobic Respiration The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
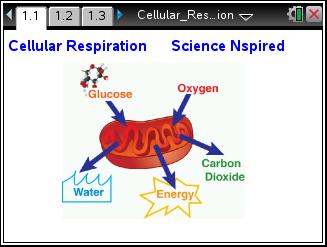



Cellular Respiration Biology Ti Science Nspired




File Cellular Respiration Simple Png Wikimedia Commons




Respiration An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
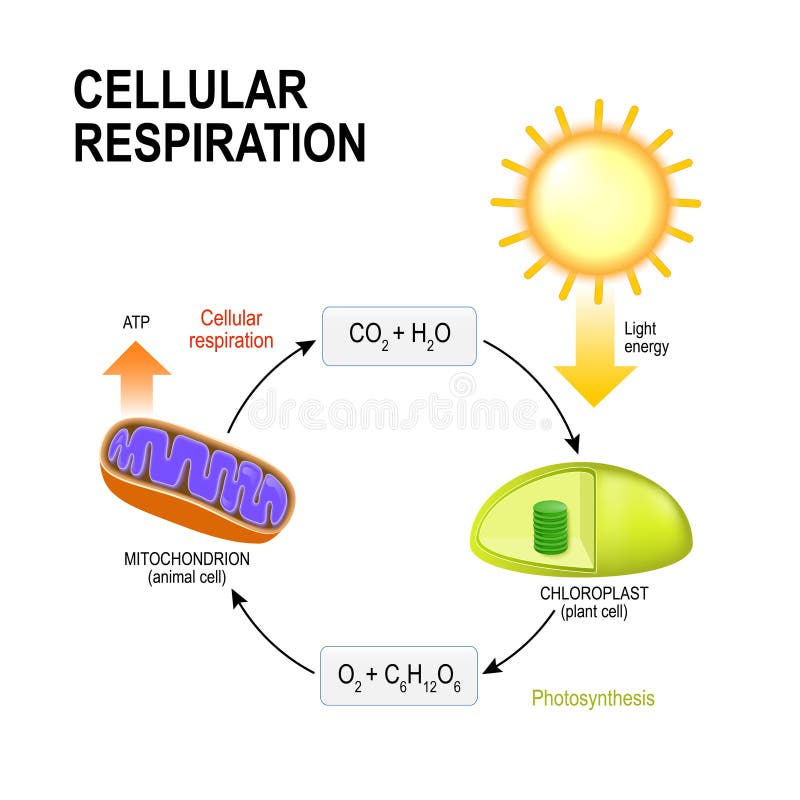



Cellular Respiration Connecting Cellular Respiration And Photos Stock Vector Illustration Of Mitochondria Mitochondrion




Burgess Lauren Unit 3 Cell Respiration




10 Differences Between Chemiosmosis In Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis
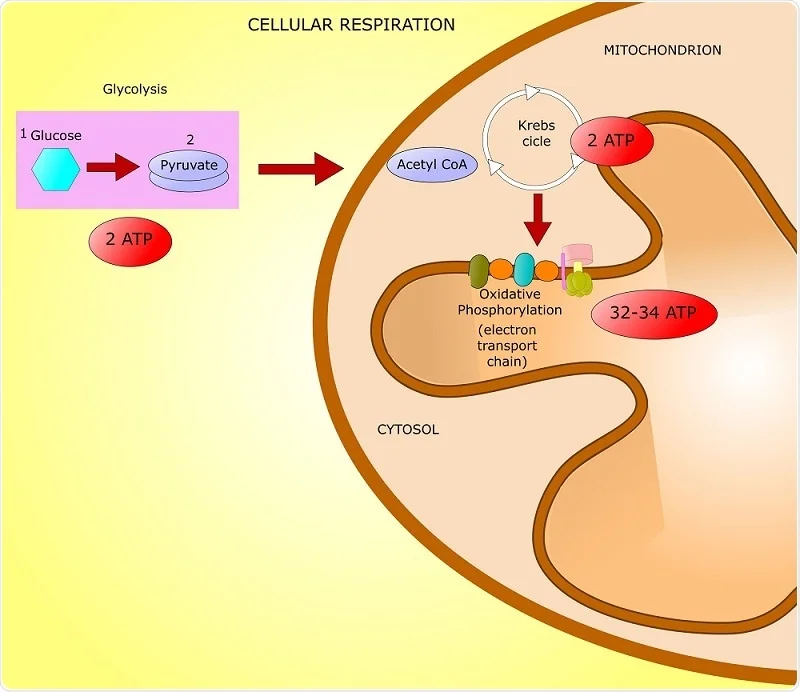



Atp Biosynthesis



Free Cellular Respiration Worksheets Homeschool Den




Cellular Respiration Equation Types Stages Products Diagrams
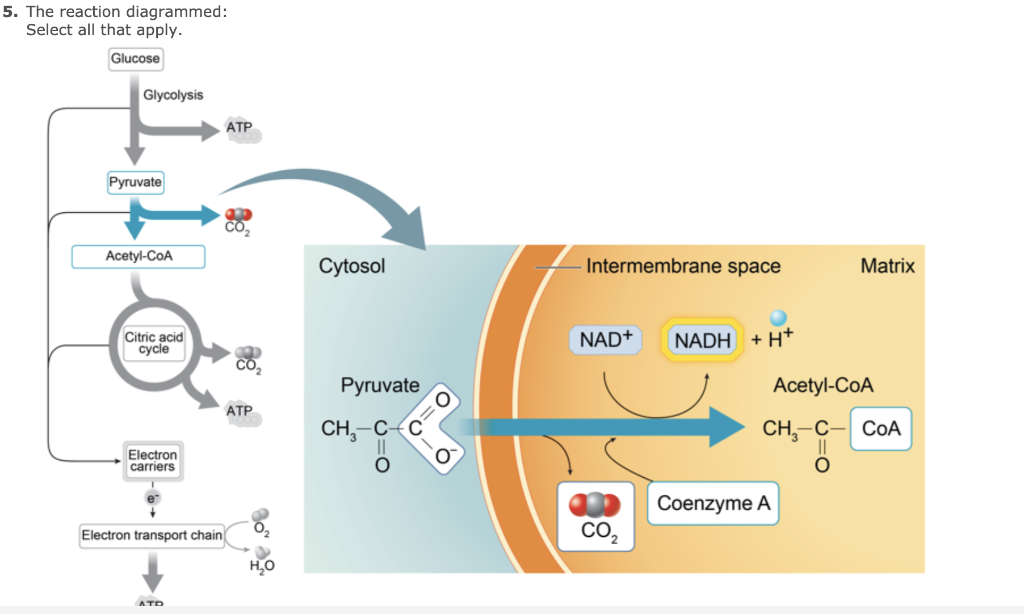



Solved 2 The Diagram Shown Represents The Four Stages Of Chegg Com



Using Models To Understand Cellular Respiration Serendip Studio



Connections Between Cellular Respiration And Other Pathways Article Khan Academy




Cellular Respiration In Mitochondria Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




7 Simplified Depiction Of Cellular Respiration Within Cytoplasm And Download Scientific Diagram



Cellular Respiration Connecting Cellular Respiration And Photos Stock Vector Illustration Of Mitochondria Mitochondrion



Cellular Respiration Biology Libretexts
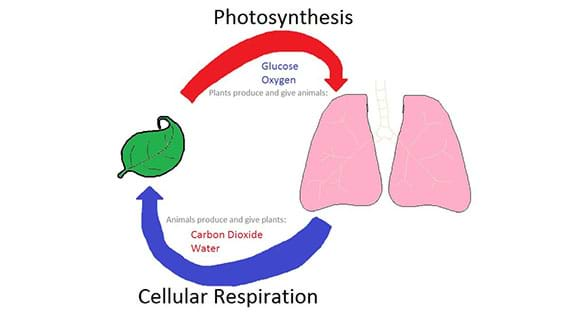



Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration At The Atomic Level Lesson Teachengineering



Cellular Respiration Vs Photosynthesis Mrs Thomas Classes




3 Stages Of Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Teaching Biology Biology Notes
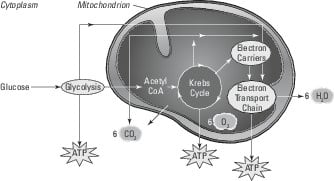



Cellular Respiration Using Oxygen To Break Down Food For Energy Dummies




Chemiosmosis And Atp Synthesis In Cellular Respiration Step By Step Simple Explanation




The Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Cycle Ms Johnston S Science Site



Sc 912 L 18 9 Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration
/Cellular-Respiration-58e52b113df78c5162b38dca.jpg)



Learn About The 3 Main Stages Of Cellular Respiration




Animal And Plant Cell Energy Cycle Vector Illustration Diagram Plant Cell Cellular Respiration Plant And Animal Cells
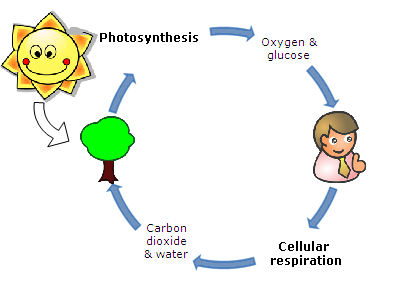



What Is The Purpose Of Cellular Respiration Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Cellular Respiration And Photosy Mindmap Eksempel
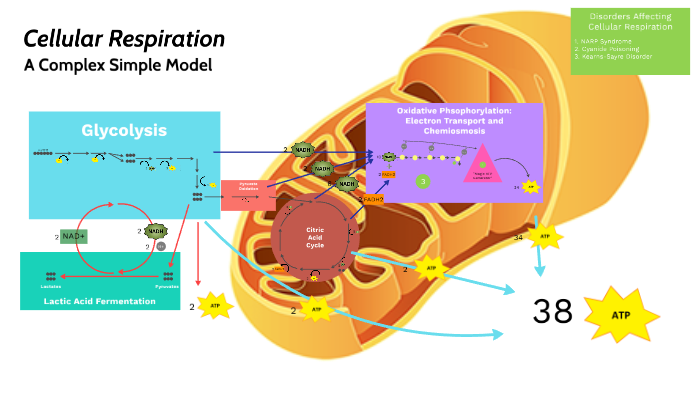



Cellular Respiration By Harvey Fortus
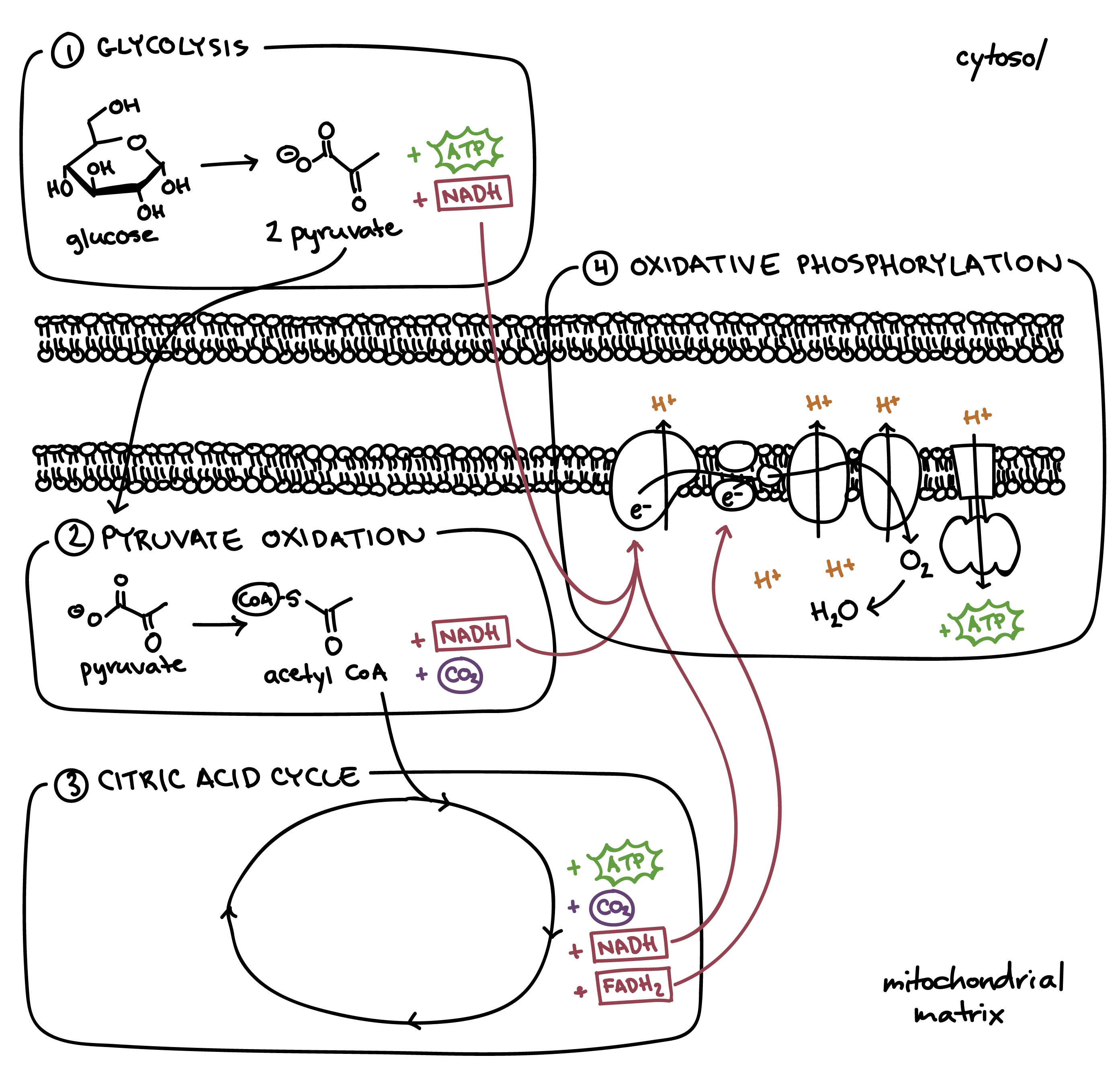



Steps Of Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy
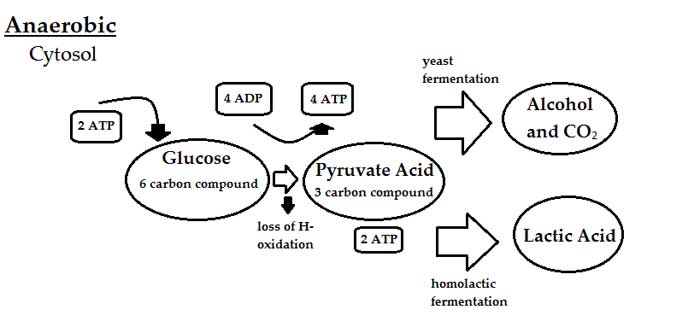



Cellular Respiration Equation Types Stages Products Diagrams




Amazon Com Newpath Learning 14 6726 Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Learning Guide Full Color Industrial Scientific




Cellular Respiration Youtube




Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis Biology Dictionary




65 Cellular Respiration Ideas Cellular Respiration Biology Cellular
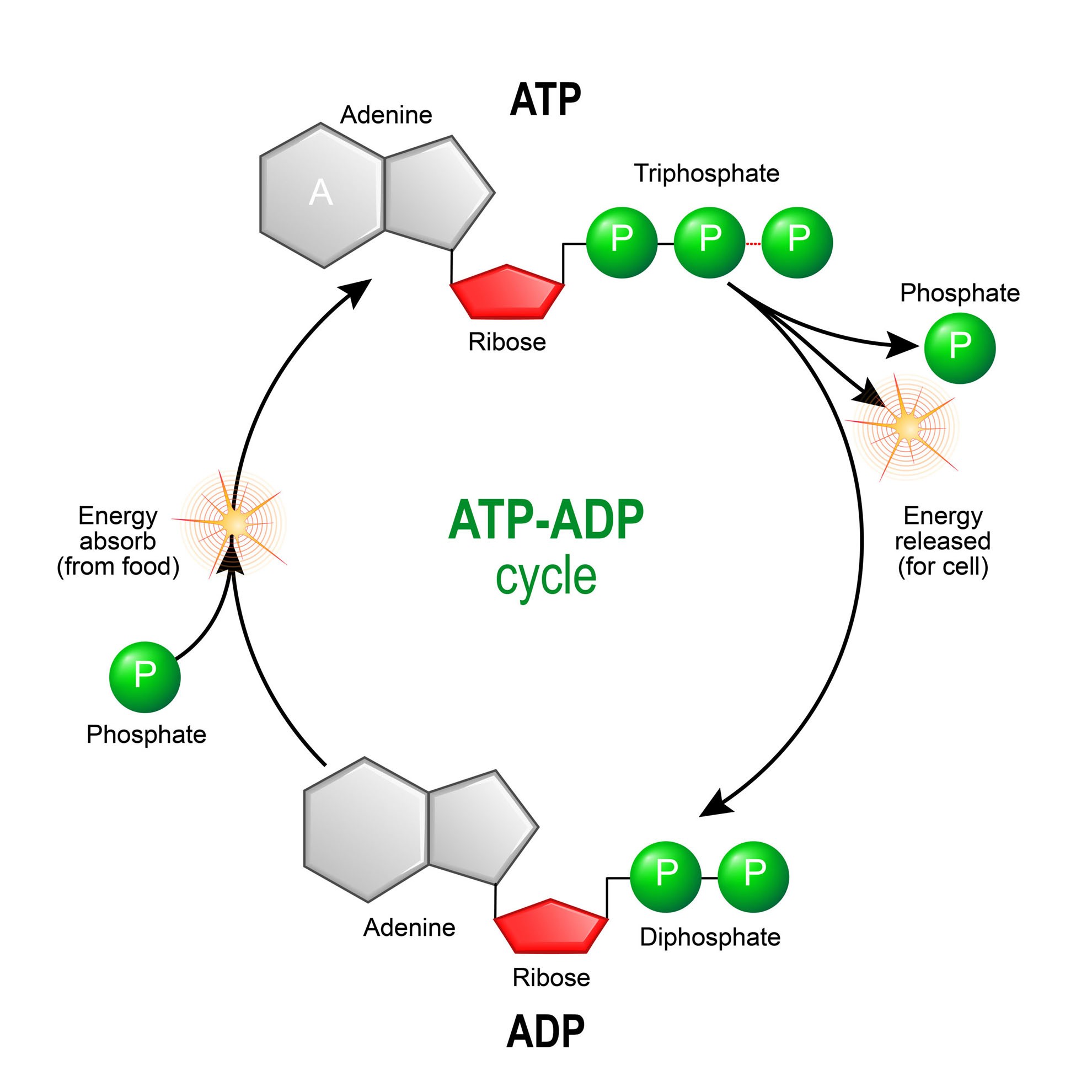



Atp Adp Biological Energy Biology Online Tutorial




A Simplified Representation Of Cellular Respiration With Its Four Main Download Scientific Diagram



Building It Up And Breaking It Down Photosynthesis Vs Cellular Respiration
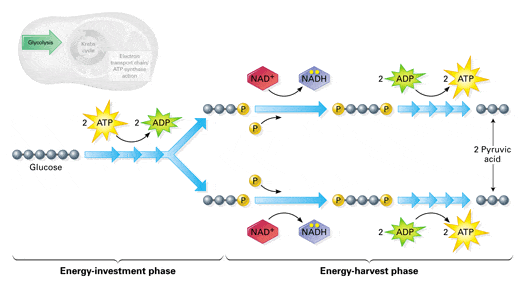



3 Simple Stages In Cellular Respiration And How They Work By Ernest Wolfe Countdown Education Medium



Jstonbraker Licensed For Non Commercial Use Only Cellular Respiration Visual
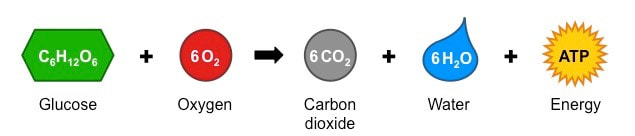



2 8 Cellular Respiration




Cells Make Atp Through Cellular Respiration Sciencemusicvideos




What Is Cellular Respiration Aerobic Anaerobic Expii




Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Diagram Quizlet




Cellular Respiration Stock Illustrations 118 Cellular Respiration Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
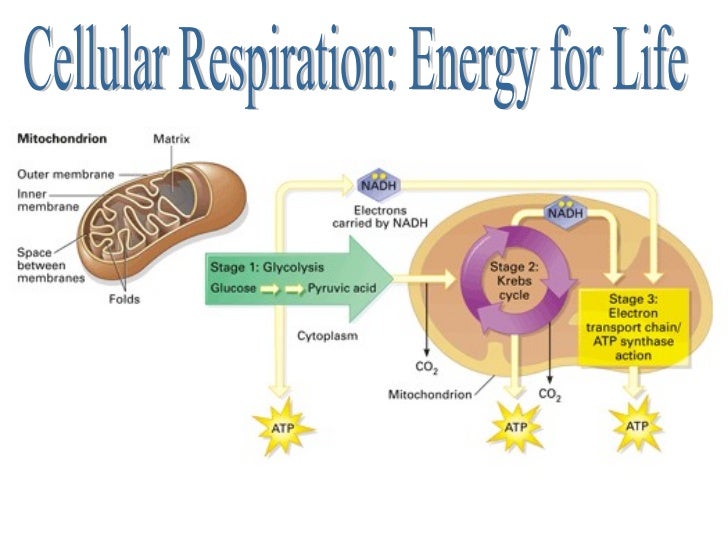



Cellular Respiration



Orise Lesson Plan Just Breathe An Introduction To Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration



5 Ways To Get Students Energized About Cellular Respiration Labster




Aerobic Cellular Respiration Easy Peasy All In One High School




A Simple Way For Students To Visualize Cellular Respiration Adapting The Board Game Mousetraptm To Model Complexity Coursesource
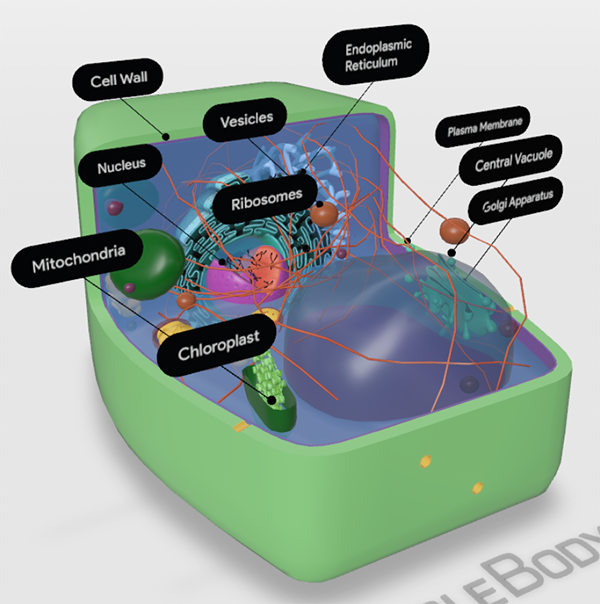



Building It Up And Breaking It Down Photosynthesis Vs Cellular Respiration
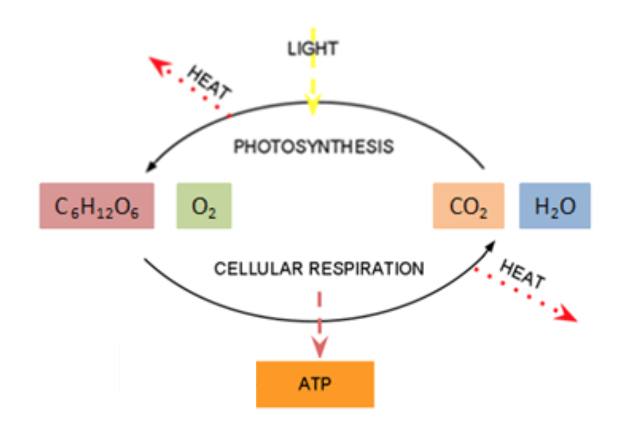



Photosynthesis And Metabolism Nutrition Science And Everyday Application
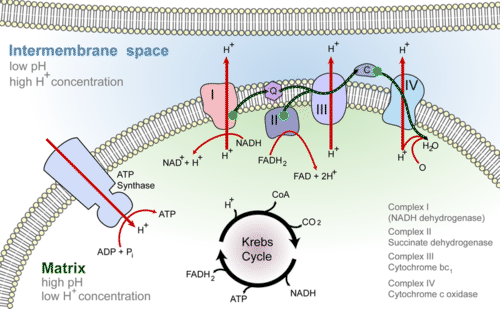



Powering The Cell Cellular Respiration Ck 12 Foundation




Photosynthesis Respiration Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Cellular Respiration 1 Cellular Respiration When Cells Break Down Simple Food Molecules Such As Glucose And Release The Energy They Contain A Molecule Ppt Download
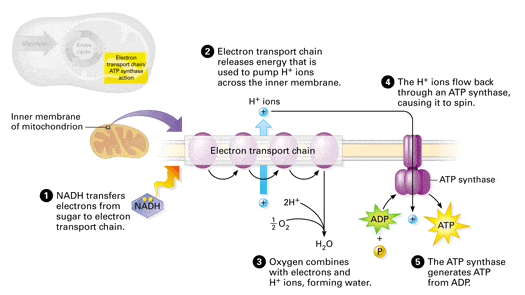



3 Simple Stages In Cellular Respiration And How They Work By Ernest Wolfe Countdown Education Medium



Cellular Respiration Energy Conversion In Animals The Institution For Science Advancement
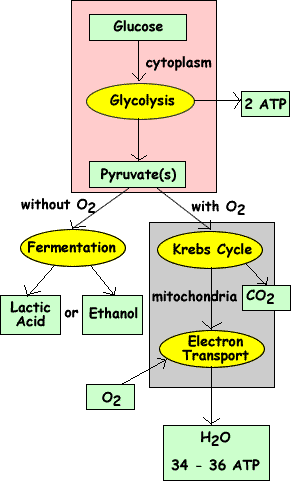



Cellular Respiration




What Is Cellular Respiration Aerobic Anaerobic Expii




Cellular Respiration Wikipedia



Metabolism Without Oxygen Boundless Biology




Discovering Cellular Respiration With Computational Modeling And Simulations Coursesource
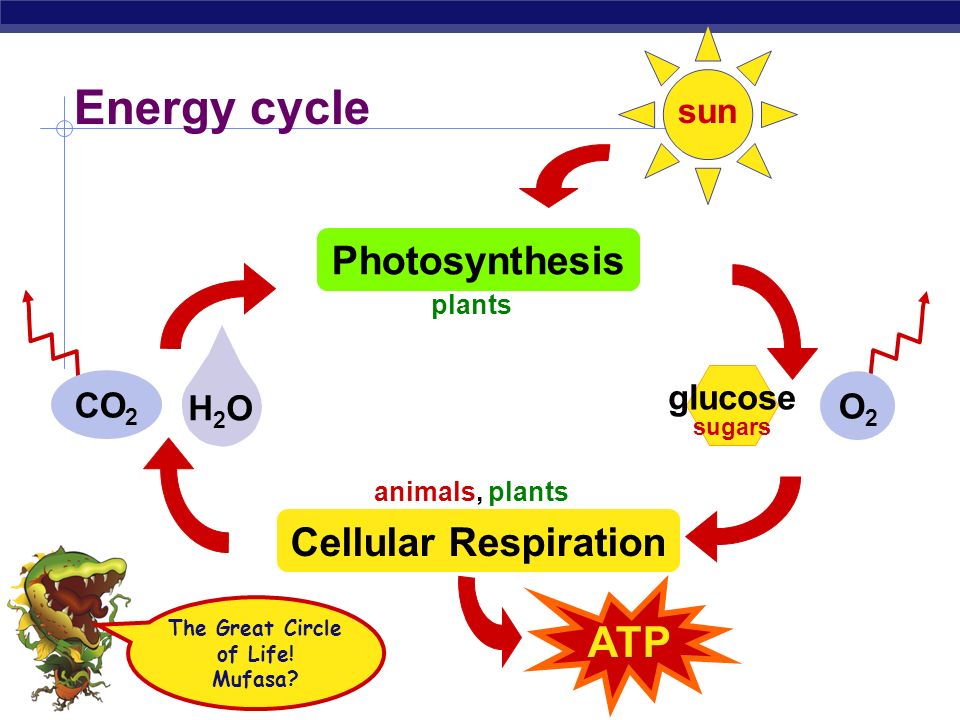



Biology Ch 4 Test Review Energy In A Cell Quiz Quizizz




Glycolysis




Cellular Respiration Process Products Britannica




Cellular Respiration Students Britannica Kids Homework Help




Cellular Respiration Steps And Pathways Youtube



4 10 Cellular Respiration Human Biology




Cellular Respiration Diagrams And Study Guide Distance Learning Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Study Guide




Aerobic Cellular Respiration Easy Peasy All In One High School
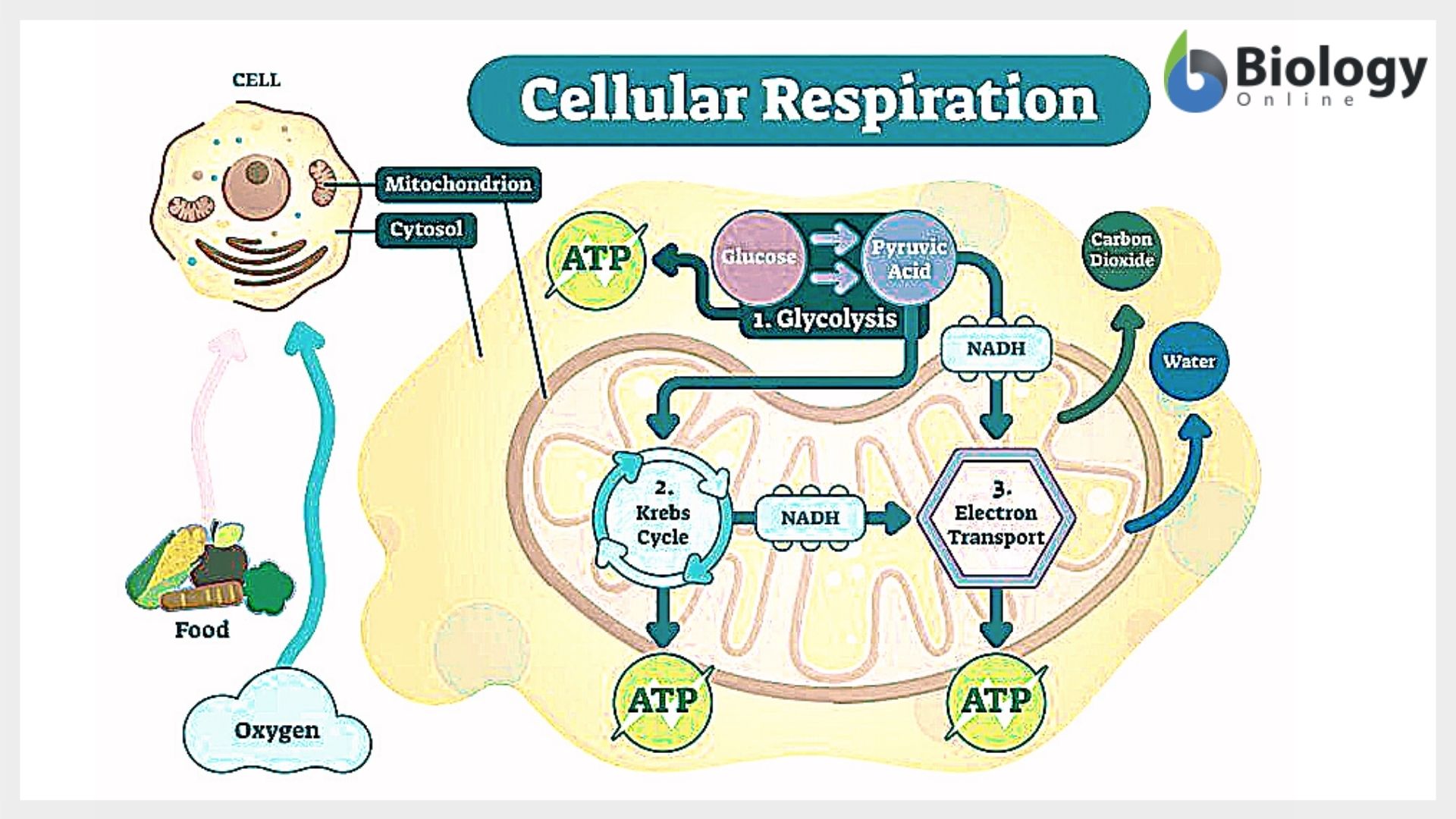



Cellular Respiration Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
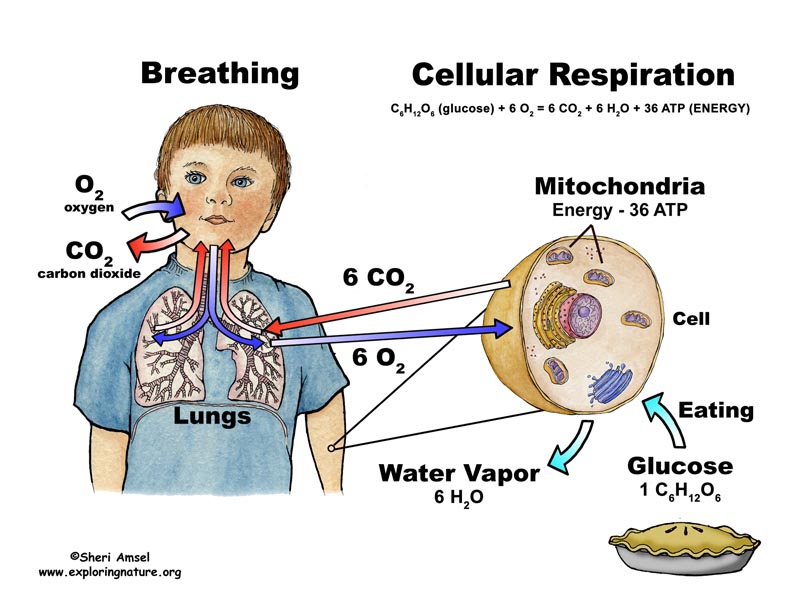



Cellular Respiration
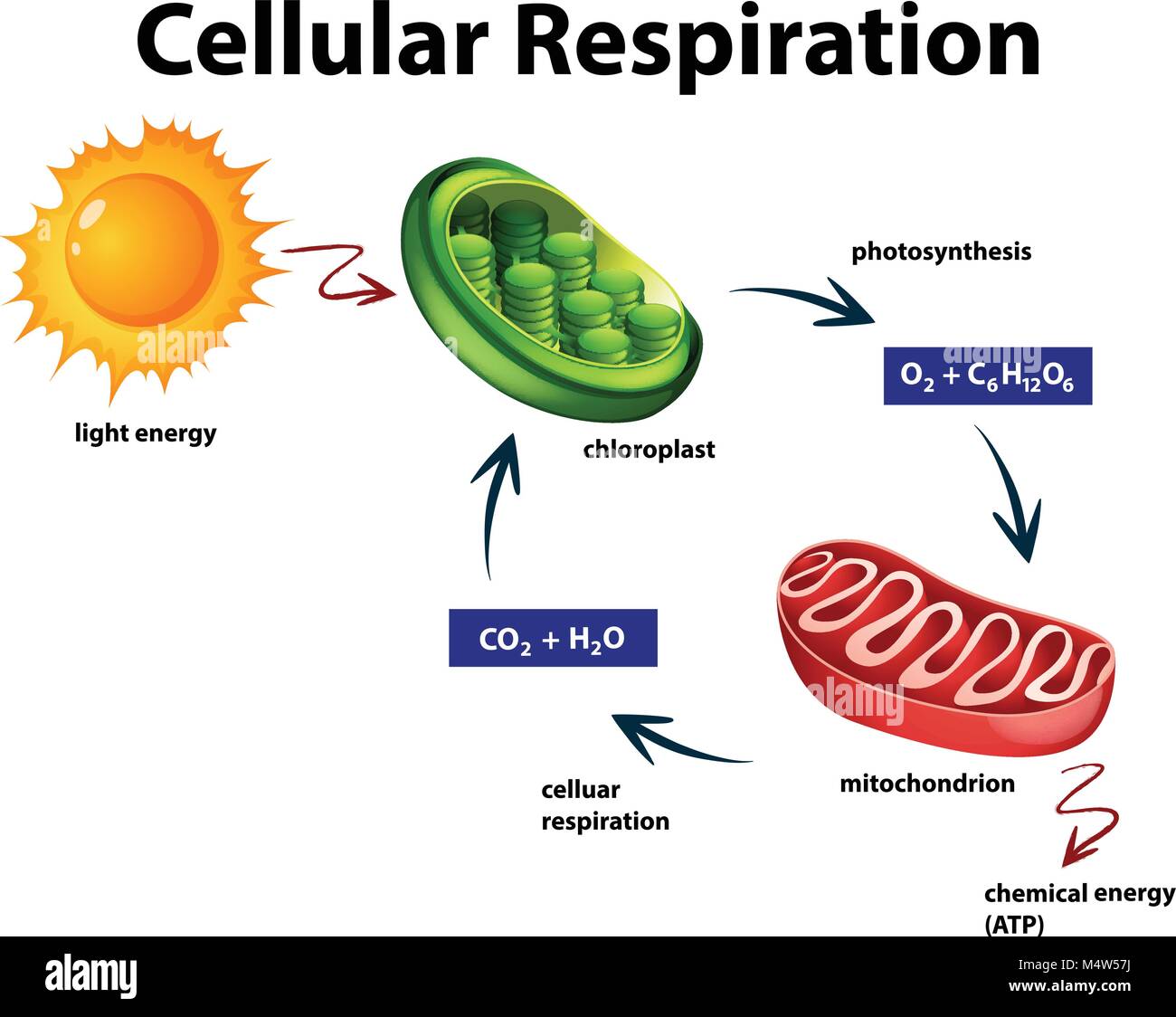



Cellular Respiration Banque D Image Et Photos Alamy




Chapter Cellular Respiration And Fermentation The Biology Primer



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿